Build Your Protocol
Soapbox creates tools that put the power back in your hands. Build your own platforms, communities, and applications with our open-source toolkit.
Empowering You to Build Freely
We're making powerful development tools accessible to everyone, advancing the future of user sovereignty and digital freedom.
100% Open Source
Complete transparency and freedom to run and modify
Decentralized First
Built on Nostr and ActivityPub for true user ownership and censorship resistance
Community Powered
Real platforms built by real people, proving decentralization works at scale
See real people are using Soapbox tools to build their communities.
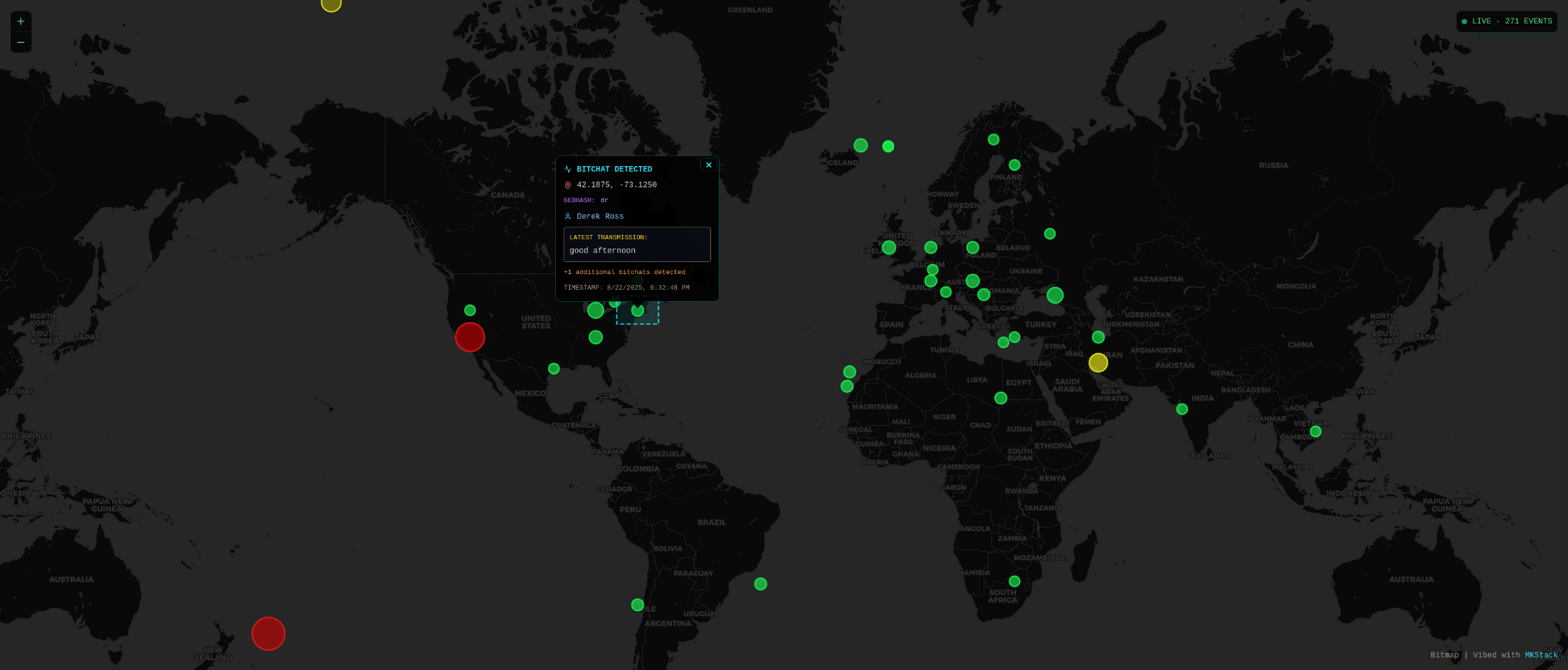
Bitmap
Real-time Bitchat monitoring and visualization of ephemeral Nostr events with geospatial analysis. A heat map application that tracks and displays anonymous, location-based messages across the Nostr network.


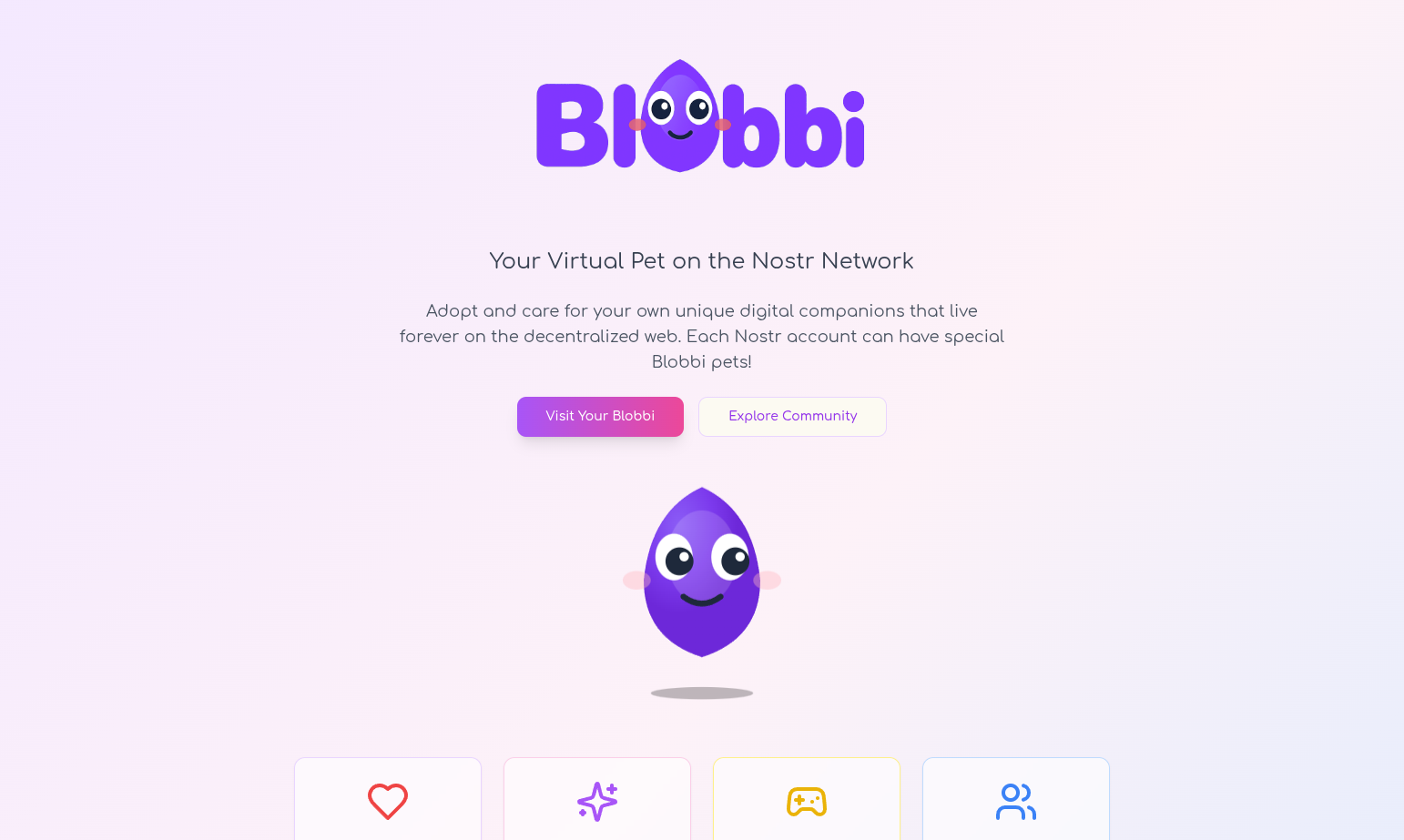
Blobbi
A decentralized virtual pet game built on the Nostr protocol. Adopt and care for unique Blobbi pets that progress through distinct life stages with structured interaction tracking and permanent milestone records.
Villager
Connect with your community to share resources, offer help, and build a stronger neighborhood together.

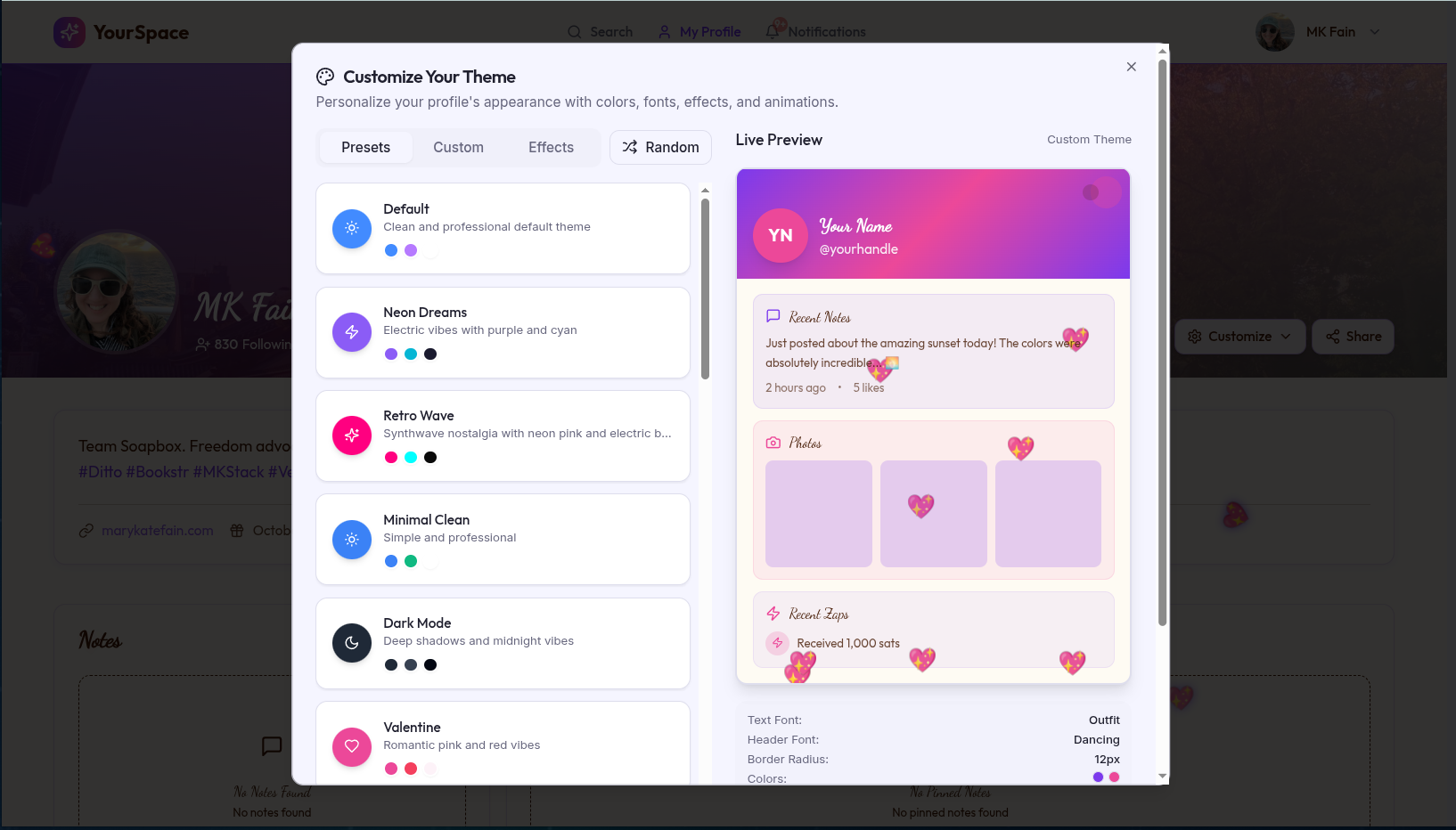
YourSpace
Bringing back the golden age of social media with modern, decentralized technology. Create your digital identity, express yourself freely, and connect with friends! 💫

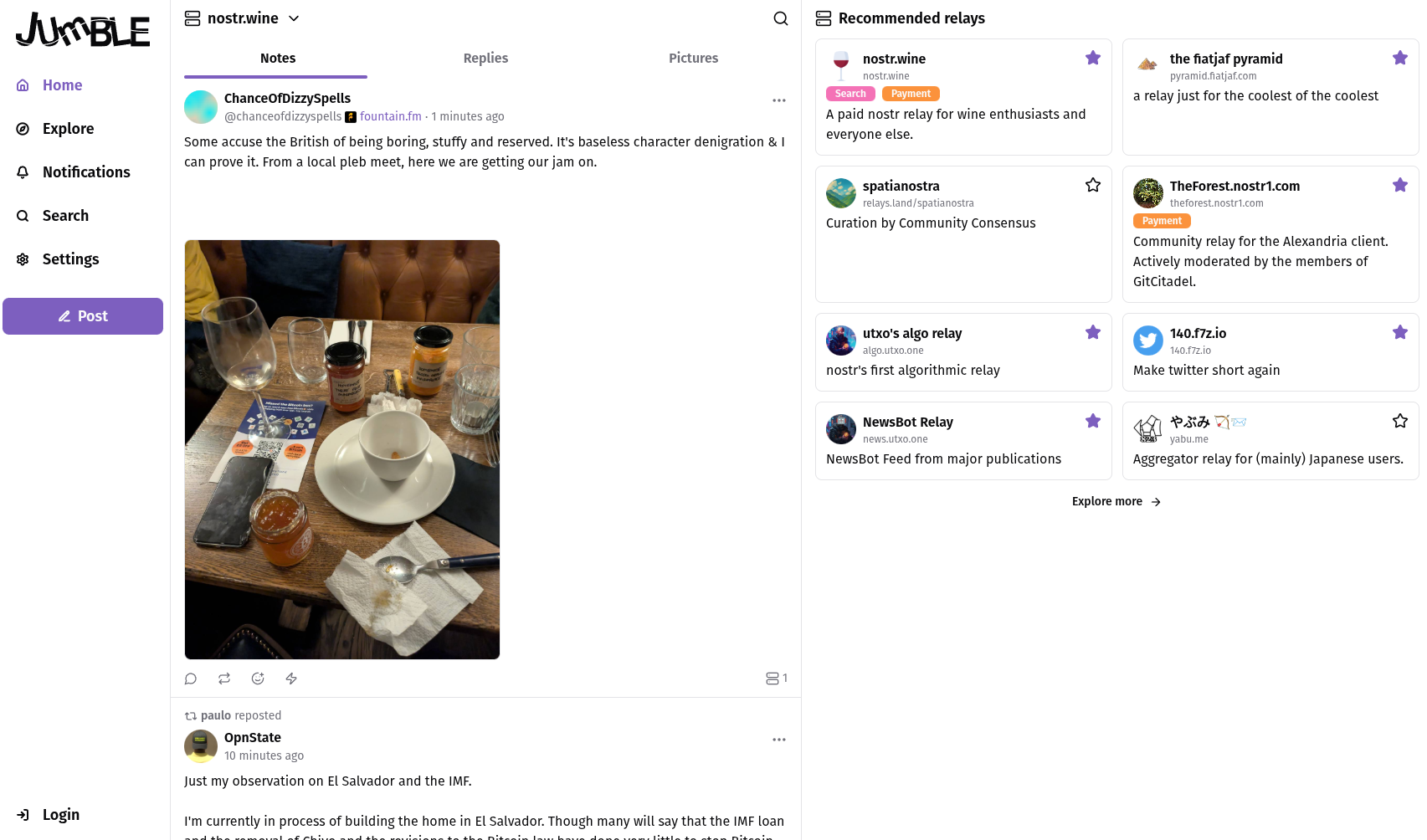
Jumble
A user-friendly Nostr client focused on relay feed browsing and relay discovery.
Agora
Agora connects freedom fighters to uncensorable international support.

Our Tools, Your Vision
From social platforms to AI development, our comprehensive suite of tools gives you everything you need to build and scale your vision.

Ditto
Community Platform Builder
Build decentralized, censorship-resistant communities on Nostr with built-in monetization and customization.

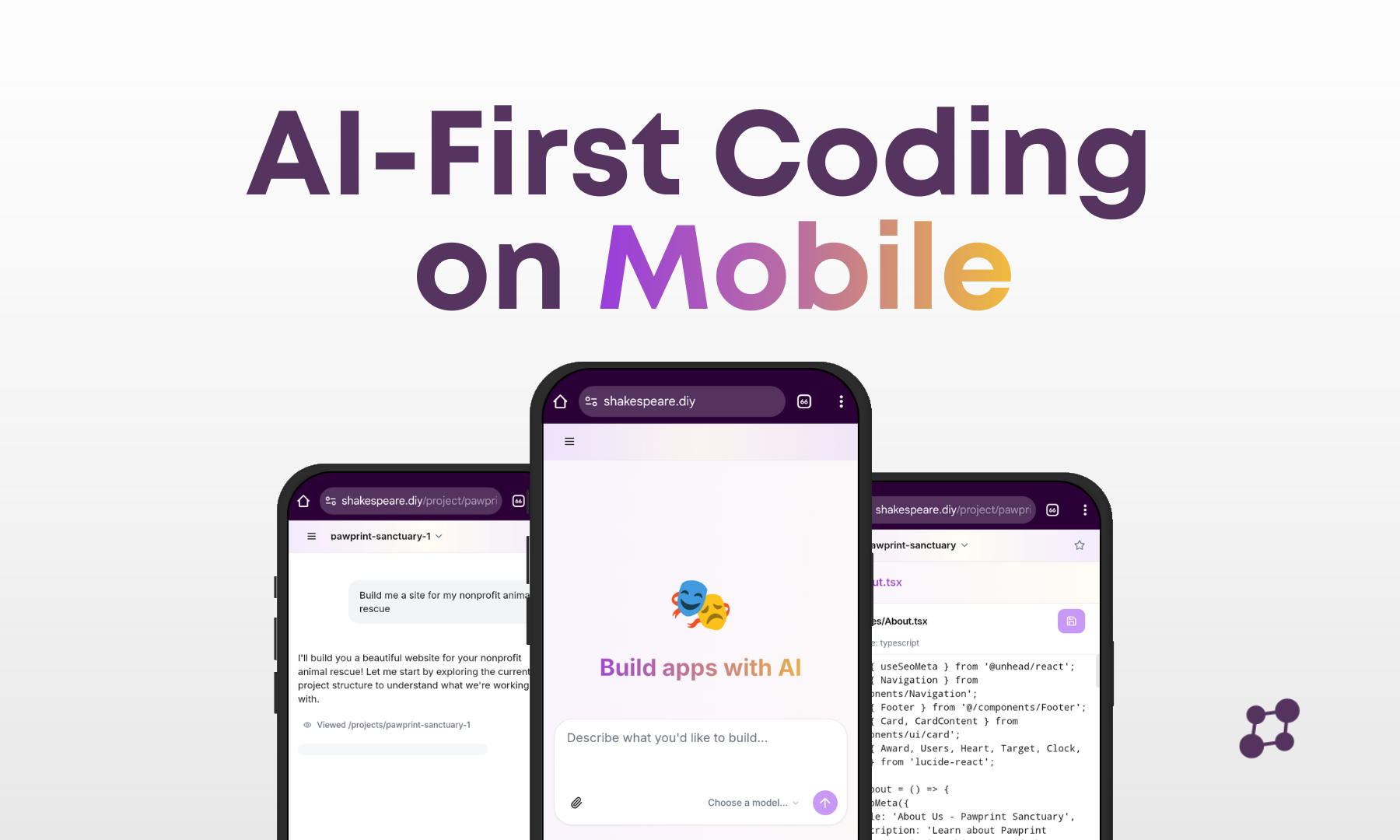
Shakespeare
AI Website Builder
Build websites and applications with AI in your browser. No downloads, any AI provider, complete freedom and control.
NostrHub
NIP Explorer
Explore and understand Nostr Improvement Proposals (NIPs) with our comprehensive database and tools for developers.
Building Bridges Across the Decentralized Web
Connecting communities across Nostr, ActivityPub, and Bluesky with Mostr
ActivityPub Bridge
Follow and interact with users across Nostr, Mastodon, Pleroma, Misskey, and other ActivityPub platforms seamlessly.
Bluesky Integration
Connect with Bluesky users through our bridge integration with Bridgy Fed, expanding your social network across protocols.
Lightning Payments
Send Bitcoin Lightning "zaps" across networks, enabling monetization and micropayments between different platforms.
Search Across the Decentralized Web
Use Mostr.pub to find and connect with users across all supported networks
Search on Mostr.pubLatest Posts from Soapbox
Stay updated with the latest insights and updates directly from the Soapbox team on Nostr.
Soapbox
Feb 24, 2026, 02:50 PM
Soapbox creates tools that put the power back in your hands. Build your own platforms, communities, and applications with our open-source toolkit for Nostr.
Soapbox
Feb 23, 2026, 03:13 PM
Soapbox creates tools that put the power back in your hands. Build your own platforms, communities, and applications with our open-source toolkit for Nostr.
Soapbox
Feb 20, 2026, 01:54 PM
Soapbox creates tools that put the power back in your hands. Build your own platforms, communities, and applications with our open-source toolkit for Nostr.
Ready to Start Building?
Choose your tool, start your project, and join the community of builders creating the decentralized future.